1、saltstack简介:
什么是saltstack?
saltstack是基于python开发的一套C/S架构配置管理工具
使用SSL证书签方的方式进行认证管理
号称世界上最快的消息队列ZeroMQ使得SaltStack能快速在成千上万台机器上进行各种操作
采用RSA Key方式确认身份
传输采用AES加密,这使得它的安全性得到了保障。
主要功能
saltstack最主要的两个功能是: 配置管理 and 远程执行
管理员能对多个操作系统进行管理
saltstack不只是一个配置管理工具,还是一个云计算与数据中心架构编排的利器
saltstack已经支持Docker相关模块
在友好地支持各大云平台之后,配合Saltstack的Mine实时发现功能可以实现各种云平台业务的自动扩展
通过部署saltstack,我们可以在成千万台服务器上做到批量执行命令,根据不同业务进行配置集中化管理、分发文件、采集服务器数据、操作系统基础及软件包管理等,saltstack是运维人员提高工作效率、规范业务配置与操作的利器。
Saltstack架构
• Saltstack基于C/S架构
- 服务器端称作Master 端口为 4506
- 客户端称作Minion 端口为 4505
- 可以实现传统处理方式,即:客户端发送请求给服务器,服务器收到请求后处理请求,再将结果返回
- 也可以使用消息队列中的发布与订阅(pub/sub)服务模式
saltstack工作原理:


Saltstack工作机制
• Master和Minion都以守护进程的方式运行
• Master监听配置文件里定义的ret_port(接收minion请求),和publish_port(发布消息)的端口
• 当Minion运行时,它会自动连接到配置文件里定义的Master地址ret_port端口进行连接认证
实现过程:
saltstack采用C/S模式server端就是salt的master,client端就是minion,minion与master>之间通过ZeroMQ消息队列通信。
minion上线后先与master端联系,把自己的pub key发过去,这时master端通过salt-key -L命令就会看到minion的key,接受该minion-key后,也就是master与minion已经互信。
master可以发送任何指令让minion执行了,salt有很多可执行模块,比如说cmd模块,>在安装minion的时候已经自带了,它们通常位于你的python库中,locate salt | grep /usr/ 可以看到salt自带的所有东西。
这些模块是python写成的文件,里面会有好多函数,如cmd.run,当我们执行salt '*' cmd.run 'uptime'的时候,master下发任务匹配到的minion上去,minion执行模块函数,并
返回结果。master监听4505和4506端口,4505对应的是ZMQ的PUB system,用来发送消息,4506对应的是REP system是来接受消息的。
具体步骤如下:
saltstack的Master与Minion之间通过ZeroMq进行消息传递,使用了ZeroMq的发布-订阅模式,连接方式包括tcp,ipc
salt命令,将cmd.run ls命令从salt.client.LocalClient.cmd_cli发布到master,获>取一个Jodid,根据jobid获取命令执行结果。
master接收到命令后,将要执行的命令发送给客户端minion。
minion从消息总线上接收到要处理的命令,交给minion._handle_aes处理
minion._handle_aes发起一个本地线程调用cmdmod执行ls命令。线程执行完ls后,调用
minion._return_pub方法,将执行结果通过消息总线返回给master
master接收到客户端返回的结果,调用master._handle_aes方法,将结果写的文件中
salt.client.LocalClient.cmd_cli通过轮询获取Job执行结果,将结果输出到终端。
2、实验过程
实验环境:
redhat6.5
关闭防火墙、iptables、setenforce
master: test1:172.25.1.11
minion: test2: 172.25.1.12
千万注意:实验开始前,实验用到的每个主机需要进行解析,否则配置文件内必须填写主机对应的ip 。
[root@test1 ~]# vim /etc/hosts
1、搭建yum 源
首先下载rhel6.5的saltstack资源包,然后配置saltstack所需的yum源(笔者这里搭建的是本地yum源,你也可以搭建网络yum源):
master端yum源
[root@foundation1 pub]# ls rhel6/ //这是已经下载好并放到pub下

[root@foundation1 pub]# scp rhel6/ root@test1:/
[root@test1 ~ ]# cd /rhel6
[root@test1 ~ ]# ls //可以看到rhel6的资源包,这里不再列出
[root@test1 rhel6]# vim /etc/yum.repos.d/rhel-source.repo
[rhel-source]
name=Red Hat Enterprise Linux $releasever - $basearch - Source
baseurl=http://172.25.1.250/rhel6.5 //网络yum源
enabled=1
gpgcheck=0
gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-redhat-release[salt]
name=saltstack
baseurl=file:///rhel6 //本地yum源,需要搭建的saltstack仓库
enabled=1
gpgcheck=0
gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-redhat-release
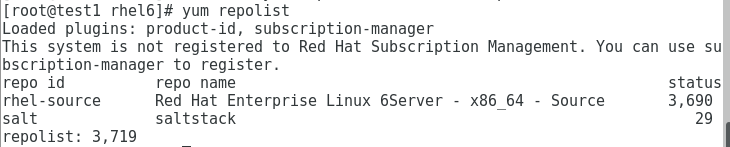
[root@test1 rhel6]# yum clean all //可以看到共有29个资源包
""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""
注意:如果不成功,可以试着这么做:
[root@test1 rhel6]# rm -rf rhel6
[root@test1 rhel6]# rm -rf repodata/
[root@test1 rhel6]# yum install -y createrepo
[root@test1 rhel6]# createrepo -v .
[root@test1 rhel6]# ls //查看会出现新的repodata目录
"""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""
minion端yum源
[root@test1 ~]# scp -r /rhel6/ root@test2:/
[root@test1 ~]# scp /etc/yum.repos.d/rhel-source.repo root@test2:/etc/yum.repos.d/
![]()
[root@test2 rhel6]# yum repolist

2、安装程序
[root@test1 ~]# yum install -y salt-master //安装master
[root@test1 ~]# /etc/init.d/salt-master start
[root@test2 ~]# yum install -y salt-minion //安装minion
若出现yum源过低的报错,可下载高一点的yum源资源包,如
提示yum版本过低,下载大于3.2.29-56版本的yum即可
yum install -y yum-3.2.29-69.el6.centos.noarch.rpm
3、配置
[root@test2 ~ ]# vim /etc/salt/minion //这里需要注意解析
![]()
[root@test2 ~]# vim /etc/hosts //解析
172.25.1.11 test1
[root@test2 ~]# /etc/init.d/salt-minion start //开启minion端的服务
交换公钥
[root@test1 ~]# salt-key -L //查看是否发现minion,发现test2
[root@test1 ~]# salt-key -A //接受并添加
[root@test1 ~]# salt-key -L //查看是否添加成功

查看公钥是否交换成功
test1端:
[root@test1 ~]# cd /etc/salt/pki/master
[root@test1 master]# md5sum master.pub

在test2端查看公钥和test1的是否相同:
[root@test2 ~]# cd /etc/salt/pki/minion/
[root@test2 minion]# ls
[root@test2 minion]# md5sum minion_master.pub
![]()

可以看出test1和test2的公钥是相同的,则密钥交换成功
在test1查看信息:
[root@test1 master]# yum install -y tree
[root@test1 master]# tree //可以看出minion端只有一个test2

4505端口是长链接:
[root@test1 master]# yum install -y lsof
[root@test1 master]# lsof -i :4505

到此,master---minion就搭建成功啦,接着开始部署lamp架构
4、简单了解YAML语法
由于编辑脚本时需要用YAML语言进行编写,所以:
默认的sls文件的renderer是YAML renderer。YAML是一个有很多强大特性的标记性语言。Salt使用了一个YAML的小型子集,映射非常常用的数据结构,像列表和字典。YAML renderer的工作是将YAML数据格式的结构编译成为python数据结构给salt使用。
只要记住三个非常简单的规则就可以使用YAML语法写sls文件了。
- 规则一: 缩进
YAML使用一个固定的缩进风格表示数据层结构关系。salt需要每个缩进级别由两个空格组成。不要使用tab键。
- 规则二: 冒号
字典的keys在YAML中的表现形式是一个以冒号结尾的字符串。values的表现形式冒号下面的每一行,用一个空格隔开:
my_key: my_value
另一种选择,一个value可以通过缩进与key联接。
my_key:
my_value注解
上面的语法是有效的YAML,但是在sls文件罕见,因为通常情况下,一个key的value不是单一的,而是一个 列表 的values。
字典可以被嵌套:
first_level_dict_key:
second_level_dict_key: value_in_second_level_dict
- 规则三: 短横杠
想要表示列表项,使用一个短横杠加一个空格。多个项使用同样的缩进
级别作为同一列表的一部分。- list_value_one
- list_value_two
- list_value_three
5、部署LAMP架构
master端
1.安装apache、php
[root@test1 ~]# vim /etc/salt/master

[root@test1 ~]# mkdir /srv/salt
[root@test1 ~]# cd /srv/salt/
[root@test1 salt]# mkdir apache
[root@test1 salt]# cd apache/
[root@test1 apache]# vim web.sls
apache-install:
pkg.installed:
- pkgs:
- httpd
- php
注意,为了实验效果,若test2已经有httpd服务请提前将test2的httpd服务卸载掉
[root@test2 ~]# yum remove httpd
[root@test1 apache]# salt test2 state.sls apache.web //master将服务推过去到test2

[root@test2 ~]# rpm -q httpd
![]()
![]()
[root@test2 ~]# rpm -q php
![]()
2.实现文件传输
[root@test1 apache]# vim web.sls
apache-install:
pkg.installed:
- pkgs:
- httpd
- php
/var/www/html/index.php:
file.managed:
- source: salt://apache/files/index.php
- mode: 644
- user: root
- group: root
[root@test1 apache]# mkdir files
[root@test1 apache]# cd files
[root@test1 files]# vim index.php //写出php的默认
<?php
phpinfo()
?>
[root@test1 files]# salt test2 state.sls apache.web //推送成功
[root@test2 ~]# cd /var/www/html/
[root@test2 html]# ls //可以发现出现了index.php
index.php
此时可以在网页进行查看:

当然配置文件也可以是:
apache-install:
pkg.installed:
- pkgs:
- httpd
- php
file.managed:
- name: /var/www/html/index.php
- source: salt://apache/files/index.php
- mode: 644
- user: root
- group: root
或者将index.php换成index.index 但是需要在master端的/srv/salt/apache/files/下提前创建好index.html
3.开启apache服务
apache-install:
pkg.installed:
- pkgs:
- httpd
- php
file.managed:
- name: /var/www/html/index.html
- source: salt://apache/files/index.html
- mode: 644
- user: root
- group: root
service.running:
- name: httpd
[root@test1 apache]# cd files
[root@test1 files]# vim index.html
<h1>index.html</h1>
[root@test1 files]# cd ..
[root@test1 apache]# salt test2 state.sls apache.web

到客户端进行查看,index.html是否远程传输过来
![]()
在网页进行访问:

3.实现服务的开机自启
[root@test1 apache]# vim web.sls
apache-install:
pkg.installed:
- pkgs:
- httpd
- php
file.managed:
- name: /var/www/html/index.php
- source: salt://apache/files/index.php
- mode: 644
- user: root
- group: root
service.running:
- name: httpd
- enable: True
- reload: True
进行测试:
推送成功,在客户端进行查看:
[root@test2 html]# chkconfig --list httpd
![]()
[root@test1 apache]# vim web.sls
apache-install:
pkg.installed:
- pkgs:
- httpd
- php
file.managed:
- name: /var/www/html/index.php
- source: salt://apache/files/index.php
- mode: 644
- user: root
- group: root
apache-service:
file.managed:
- name: /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
- source: salt://apache/files/httpd.conf
service.running:
- name: httpd
- enable: True
- reload: True
- watch:
- file: apache-service
[root@test1 apache]# cd files
[root@test1 files]# cp /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf . //否则会有报错
[root@test1 files]# ls
httpd.conf index.html index.php
[root@test1 files]# cd ..
[root@test1 apache]# salt test2 state.sls apache.web
推送成功
此时apache服务的端口为80

尝试将服务器端的apache配置文件端口由80更改为8080
[root@test1 apache]# cd files/
[root@test1 files]# vim httpd.conf

再次推送
[root@test1 apache]# salt test2 state.sls apache.web //推送成功
在客户端查看:
[root@test2 html]# netstat -antlp | grep httpd
![]()
[root@test1 apache]# vim install.sls
apache-install:
pkg.installed:
- pkgs:
- httpd
- php
file.managed:
- name: /var/www/html/index.php
- source: salt://apache/files/index.php
- mode: 644
- user: root
- group: root
[root@test1 apache]# vim service.sls
include:
- apache.install
apache-service:
file.managed:
- name: /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
- source: salt://apache/files/httpd.conf
service.running:
- name: httpd
- enable: True
- reload: True
- watch:
- file: apache-service
[root@test1 apache]# cd files/
[root@test1 files]# vim httpd.conf

一键推送
[root@test1 files]# salt test2 state.sls apache.service //推送成功
在test2上查看
[root@test2 html]# netstat -antlp | grep httpd
![]()
6.一键部署nginx
root@test1 salt]# ls
apache
[root@test1 salt]# mkdir nginx
[root@test1 salt]# cd nginx/
[root@test1 nginx]# mkdir files
[root@test1 nginx]# cd files/
[root@test1 files]# cp /root/nginx-1.14.0.tar.gz . //注意:这里需要用到nginx源码包,请提前将其下载下来并放到/root下以便拷贝
[root@test1 files]# touch nginx
[root@test1 files]# ls
![]()
![]()
[root@test1 files]# cd ..
[root@test1 nginx]# vim install.sls
nginx-install:
pkg.installed:
- pkgs:
- pcre-devel
- openssl-devel
- gcc
file.managed:
- name: /mnt/nginx-1.14.0.tar.gz
- source: salt://nginx/files/nginx-1.14.0.tar.gz
cmd.run:
- name: cd /mnt && tar zxf nginx-1.14.0.tar.gz && cd nginx-1.14.0 && sed -i.bak 's/#define NGINX_VER "nginx\/" NGINX_VERSION/#define NGINX_VER "nginx"/g' src/core/nginx.h && sed -i.bak 's/CFLAGS="$CFLAGS -g"/#CFLAGS="$CFLAGS -g"/g' auto/cc/gcc && ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx --with-http_ssl_module --with-http_stub_status_module --with-threads --with-file-aio &> /dev/null && make &> /dev/null && make install &> /dev/null
- creates: /usr/local/nginx //表示当系统有nginx文件时不进行重复安装与编译
[root@test1 nginx]# salt test2 state.sls nginx.install //远程调用执行成功
现在在客户端进行查看:
[root@test2 ~]# ps -ax //快速抓拍可以看到正在编译等

[root@test2 minion]# cd /mnt/
[root@test2 mnt]# ls
让服务自动运行:
重新编写脚本,保证一个脚本负责源码编译,一个脚本负责运行服务,以便更好的管理:
[root@test1 srv]# cd
[root@test1 ~]# cd /srv/salt/
[root@test1 salt]# ls
apache nginx
[root@test1 salt]# cd nginx/
[root@test1 nginx]# ls
files install.sls
[root@test1 nginx]# vim service.sls //目的是得到nginx的配置文件,让服务自动运行
include:
- nginx.install
nginx-service:
cmd.run:
- name: /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
[root@test1 nginx]# salt test2 state.sls nginx.service //推送成功
此时查看服务是否已经运行:
[root@test2 ~]# netstat -antlp | grep nginx //可以看到端口号为80的进程
![]()
[root@test1 files]# cd ..
[root@test1 nginx]# cd files/
[root@test1 files]# vim nginx //在/srv/salt/nginx/file目录下写一个nginx脚本,用来调用nginx服务
#!/bin/sh
# nginx Startup script for nginx
# chkconfig: - 85 15
# processname: nginx
# config: /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx/nginx.conf
# pidfile: /usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid
# description: nginx is an HTTP and reverse proxy server
### BEGIN INIT INFO
# Provides: nginx
# Required-Start: $local_fs $remote_fs $network
# Required-Stop: $local_fs $remote_fs $network
# Default-Start: 2 3 4 5
# Default-Stop: 0 1 6
# Short-Description: start and stop nginx
### END INIT INFO# Source function library.
. /etc/rc.d/init.d/functionsif [ -L $0 ]; then
initscript=`/bin/readlink -f $0`
else
initscript=$0
fi#sysconfig=`/bin/basename $initscript`
#if [ -f /etc/sysconfig/$sysconfig ]; then
# . /etc/sysconfig/$sysconfig
#finginx=${NGINX-/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx}
prog=`/bin/basename $nginx`
conffile=${CONFFILE-/usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf}
lockfile=${LOCKFILE-/var/lock/subsys/nginx}
pidfile=${PIDFILE-/usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid}
SLEEPMSEC=${SLEEPMSEC-200000}
UPGRADEWAITLOOPS=${UPGRADEWAITLOOPS-5}
RETVAL=0start() {
echo -n $"Starting $prog: "daemon --pidfile=${pidfile} ${nginx} -c ${conffile}
RETVAL=$?
echo
[ $RETVAL = 0 ] && touch ${lockfile}
return $RETVAL
}stop() {
echo -n $"Stopping $prog: "
killproc -p ${pidfile} ${prog}
RETVAL=$?
echo
[ $RETVAL = 0 ] && rm -f ${lockfile} ${pidfile}
}reload() {
echo -n $"Reloading $prog: "
killproc -p ${pidfile} ${prog} -HUP
RETVAL=$?
echo
}upgrade() {
oldbinpidfile=${pidfile}.oldbinconfigtest -q || return
echo -n $"Starting new master $prog: "
killproc -p ${pidfile} ${prog} -USR2
echofor i in `/usr/bin/seq $UPGRADEWAITLOOPS`; do
/bin/usleep $SLEEPMSEC
if [ -f ${oldbinpidfile} -a -f ${pidfile} ]; then
echo -n $"Graceful shutdown of old $prog: "
killproc -p ${oldbinpidfile} ${prog} -QUIT
RETVAL=$?
echo
return
fi
doneecho $"Upgrade failed!"
RETVAL=1
}configtest() {
if [ "$#" -ne 0 ] ; then
case "$1" in
-q)
FLAG=$1
;;
*)
;;
esac
shift
fi
${nginx} -t -c ${conffile} $FLAG
RETVAL=$?
return $RETVAL
}rh_status() {
status -p ${pidfile} ${nginx}
}# See how we were called.
case "$1" in
start)
rh_status >/dev/null 2>&1 && exit 0
start
;;
stop)
stop
;;
status)
rh_status
RETVAL=$?
;;
restart)
configtest -q || exit $RETVAL
stop
start
;;
upgrade)
rh_status >/dev/null 2>&1 || exit 0
upgrade
;;
condrestart|try-restart)
if rh_status >/dev/null 2>&1; then
stop
start
fi
;;
force-reload|reload)
reload
;;
configtest)
configtest
;;
*)
echo $"Usage: $prog {start|stop|restart|condrestart|try-restart|force-reload|upgrade|reload|status|help|configtest}"
RETVAL=2
esacexit $RETVAL
[root@test2 ~]# scp /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf root@test1:/srv/salt/nginx/files //将test2的服务配置文件发送给test1
将/srv/salt/nginx/files/nginx.conf进行更改:
[root@test1 nginx]# cd files/
[root@test1 files]# ls
![]()
创建用户
[root@test1 files]# vim nginx.conf
user nginx nginx;

[root@test1 files]# cd /srv/salt/
[root@test1 salt]# mkdir users
[root@test1 salt]# cd users/
[root@test1 users]# ls
[root@test1 users]# vim nginx.sls
nginx-group:
group.present:
- name: nginx
- gid: 800
nginx-user:
user.present:
- name: nginx
- uid: 800
- gid: 800
- shell: /sbin/nologin //指定shell
- createhome: False
- home: /usr/local/nginx //指定家目录
[root@test1 users]# cd ..
[root@test1 salt]# cd nginx/
[root@test1 nginx]# ls
files install.sls service.sls
[root@test1 nginx]# vim service.sls
include:
- users.nginx
- nginx.install
/usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf:
file.managed:
- source: salt://nginx/files/nginx.conf
nginx-service:
file.managed:
- name: /etc/init.d/nginx
- source: salt://nginx/files/nginx
- mode: 755
service.running:
- name: nginx
- reload: True
- watch:
- file: /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
[root@test1 nginx]# salt test2 state.sls nginx.service //再次将其推给test2
注意:可提前将test2的nginx服务关掉
[root@test2 usr]# /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s stop
[root@test1 files]# salt test2 state.sls nginx.service //推送成功
[root@test2 usr]# netstat -antlp | grep nginx

查看test2前后的变化:
[root@test2 ~]# id nginx //推送前
[root@test2 ~]# id nginx
id: nginx: No such user
[root@test2 ~]# id nginx //推送后
![]()
![]()
为了方便源码编译其他tar包时需要安装依赖性,将依赖性工具进行打包,简化步骤:
[root@test1 nginx]# cd ..
[root@test1 salt]# mkdir pkgs
[root@test1 salt]# cd pkgs/
[root@test1 pkgs]# vim make.sls
[root@test1 pkgs]# ls
make.sls
[root@test1 pkgs]# cd ..
[root@test1 salt]# ls
apache nginx pkgs users
[root@test1 salt]# cd nginx/
[root@test1 nginx]# ls
files install.sls service.sls
[root@test1 nginx]# vim install.sls
include:
- pkgs.make //直接导入make包,避免当多个源码编译都用到make里面的安装包时都得重新写一遍
nginx-install:
file.managed:
- name: /mnt/nginx-1.14.0.tar.gz
- source: salt://nginx/files/nginx-1.14.0.tar.gz
cmd.run:
- name: cd /mnt && tar zxf nginx-1.14.0.tar.gz && cd nginx-1.14.0 && sed -i.bak 's/#define NGINX_VER "nginx\/" NGINX_VERSION/#define NGINX_VER "nginx"/g' src/core/nginx.h && sed -i.bak 's/CFLAGS="$CFLAGS -g"/#CFLAGS="$CFLAGS -g"/g' auto/cc/gcc && ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx --with-http_ssl_module --with-http_stub_status_module --with-threads --with-file-aio &> /dev/null && make &> /dev/null && make install &> /dev/null
- creates: /usr/local/nginx
grains、pillar、Jinja模块的使用(作用相同)
!!!温馨提示:下面这段是练习模块,若需要搭建高可用架构可以直接跳过,继续下一段动作。
例如用grains模块:
在minion端配置
在托管主机上修改
[root@test1 salt]# vim /etc/salt/minion //test1端将roles:对应的参数改为想要配置的服务
[root@test2 ~]# vim /etc/salt/minion //test2端将roles:对应的参数改为想要配置的服务
[root@test2 ~]# /etc/init.d/salt-minion restart
[root@test1 salt]# /etc/init.d/salt-minion restart
[root@test1 salt]# salt '*' grains.item roles //可以看见roles对应的服务
[root@test1 salt]# vim top.sls
base:
'test3':
- haproxy.service
'roles:apache': //和apache匹配的roles推送apache
- match: grain
- apache.service
'roles:nginx': //和nginx匹配的roles推送nginx
- match: grain
- nginx.service[root@test1 keepalived]# salt '*' state.highstate //一键推送,此时查看可以看到test1和test2端推送上了nginx和apache服务
再如pillar模块:(注意:pillar和grains模块没有什么联系,但可以结合使用)
pillar模块在master配置
[root@test1 salt]# vim /etc/salt/master
[root@test1 salt]# /etc/init.d/salt-master restart
[root@test1 srv]# mkdir pillar/ //创建pillar目录
[root@test1 srv]# cd pillar/
[root@test1 pillar]# mkdir web
[root@test1 pillar]# cd web/[root@test1 web]# vim install.sls
{ % if grains[' fqdn '] == 'test2' % } //与test2匹配的主机推送apache
webserver: apache
{ % elif grains[' fqdn '] == 'test1' % } //与test1匹配的主机推送nginx
webserver: nginx
{ % endif % }[root@test1 web]# cd ..
[root@test1 pillar]# vim top.sls //这个文件必须要写
base:
'*':
- web.install然后一键推送,成功
[root@test2 ~]# netstat -antlp | grep 80
Jinja模块的使用
例如:需要端口是变量,可以随时改变,那么就需要用到Jinja这个模块
[root@test1 pillar]# cd /srv/salt/apache/files/
[root@test1 files]# vim httpd.conf
[root@test1 files]# cd ..
[root@test1 apache]# vim service.sls
include:
- apache.installapache-service:
file.managed:
- name: /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
- source: salt://apache/files/httpd.conf
- template: jinja
- context:
port: 80
bind: 172.25.1.12service.running:
- name: httpd
- enable: True
- reload: True
- watch:
- file: apache-service[root@test1 apache]# salt test2 state.sls apache.service
[root@test2 ~]# netstat -antlp | grep httpd //推送过去之后查看端口变化
[root@test2 ~]# vim /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf //配置文件也相应变化
再如只修改端口为任意数:
apache配置文件内将80修改为{{ port }}
更改service.sls,添加到file.managed:后面
- template: jinja
- context:
port: 8080
一键推送,推送成功以后修改端口只需要修改service.sls的port对应的参数为其它数然后一键推送即可。
到此这部分就结束啦
别忘记接着来看下一篇哦!