实验1 谓词表示法与产生式知识表示
一、实验目的
1、熟悉谓词逻辑表示法;
2、理解和掌握产生式知识表示方法,实现产生式系统的规则库。
二、实验内容
要求通过C/C++/python语言编程实现:
1、猴子摘香蕉问题
2、动物识别系统
(1)建立识别七种动物识别系统的规则;
(2)确定需要识别的动物及其属性(7种动物,即:老虎、金钱豹、斑马、长颈鹿、企鹅、鸵鸟和信天翁)。
三、问题描述
1、房子里有一只猴子(即机器人),位于a处。在c处上方的天花板上有一串香蕉,猴子想吃,但摘不到。房间的b处还有一个箱子,如果猴子站到箱子上,就可以摸着天花板。如图1所示,对于上述问题,可以通过谓词逻辑表示法来描述知识。实现猴子摘香蕉问题的求解过程。
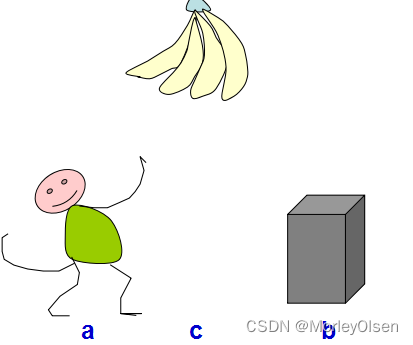
图1 猴子摘香蕉问题
2、建立一个动物识别系统的规则库,编写程序用以识别虎、豹、斑马、长颈鹿、企鹅、鸵鸟、信天翁等7种动物。
为了识别这些动物,可以根据动物识别的特征,建立包含下述规则库:
R1:if 动物有毛发 then 动物是哺乳动物
R2:if 动物有奶 then 动物是哺乳动物
R3:if 动物有羽毛 then 动物是鸟
R4:if 动物会飞 and 会生蛋 then 动物是鸟
R5:if 动物吃肉 then 动物是食肉动物
R6:if 动物有犀利牙齿 and 有爪 and 眼向前方 then 动物是食肉动物
R7:if 动物是哺乳动物and有蹄then动物是有蹄类动物
R8:if 动物是哺乳动物and反刍then动物是有蹄类动物
R9:if 动物是哺乳动物and是食肉动物and有黄褐色 and 有暗斑点 then 动物是豹
R10:if 动物是哺乳动物 and是食肉动物and有黄褐色 and有黑色条纹 then 动物是虎
R11:if动物是有蹄类动物 and 有长脖子and有长腿and有暗斑点 then 动物是长颈鹿
R12:if 动物是有蹄类动物 and有黑色条纹 then 动物是斑马
R13:if 动物是鸟and不会飞 and有长脖子and有长腿 and有黑白二色 then 动物是鸵鸟
R14:if 动物是鸟 and不会飞 and会游泳 and有黑白二色 then 动物是企鹅
R15:if 动物是鸟 and善飞 then 动物是信天翁
四、编写程序并调试(源程序、实验过程与结果)
1:猴子摘香蕉问题
1.1:源程序
| dict = {} count = 0 while 1: if count == 3: break item = input("please input your item:") site = input("please input your site:") if item != 'monkey' and item != 'box' and item != 'banana': print("input error") else: dict.setdefault(item, site) count += 1 print() # change lines step = 1 #initialzie step climb = 0 gain = 0 # if monkey is not at box site if dict['monkey'] != dict['box']: result = "step"+str(step)+": move monkey to box" print(result,end=" ") print(dict['monkey']+"->"+dict['box']) dict['monkey']=dict['box'] step += 1 # if box is not at banana site if dict['box'] != dict['banana']: result = "step"+str(step)+": move box to banana" print(result,end=" ") print(dict['box']+"->"+dict['banana']) dict['box']=dict['banana'] dict['monkey']=dict['banana'] step += 1 # monkey climbs onto the box if climb == 0: result = "step"+str(step)+": monkey climbs on the box" print(result,end=" ") print(dict['monkey']+"->"+dict['box']) step += 1 climb = 1 # monkey jumps to get the banana if climb == 1 and gain == 0: result = "step"+str(step)+": monkey jumps to get the banana" print(result,end=" ") print(dict['box']+"->"+dict['banana']) step += 1 gain = 1 |
1.2:实验过程与结果

如下图所示,依次输入三个物体及其地点,例如猴子在a点、箱子在b点、香蕉在c点。输入完毕后,程序自动显示每一步的操作。
以图中的结果为例,第一步命令猴子移动到箱子处,即a点到b点;第二步命令猴子将箱子移动到香蕉处,即b点到c点;第三步命令猴子爬到箱子上,地点不变;第四步命令猴子跳起来拿到香蕉,地点不变。综上所述,通过上述4个步骤即可实现猴子拿到香蕉的结果。
2:动物识别系统
2.1:源程序
| dict = {} dict.setdefault(1, "有毛发") dict.setdefault(2, "有奶") dict.setdefault(3, "有羽毛") dict.setdefault(4, "会飞") dict.setdefault(5, "会生蛋") dict.setdefault(6, "吃肉") dict.setdefault(7, "犀利牙齿") dict.setdefault(8, "有爪") dict.setdefault(9, "眼向前方") dict.setdefault(10, "有蹄") dict.setdefault(11, "反刍") dict.setdefault(12, "有黄褐色") dict.setdefault(13, "有暗斑点") dict.setdefault(14, "有黑色条纹") dict.setdefault(15, "有长脖子") dict.setdefault(16, "有长腿") dict.setdefault(17, "不会飞") dict.setdefault(18, "有黑白二色") dict.setdefault(19, "会游泳") dict.setdefault(20, "善飞") mammal = 0 # 哺乳动物 bird = 0 # 鸟 meat = 0 # 食肉动物 foot = 0 # 蹄类动物 print(dict) print("please later input features according to this directory") feature = [] n = int(input("please input the total number of your features: ")) # add int() to convert str into int, or error will occur for i in range(n): t = int(input("please input your current feature number: ")) feature.append(t) # hash features hash = [] for i in range(21): hash.append(0) for item in feature: hash[item]=1 # rules result = "" check = 0 # rule 1 2 if hash[1] == 1 or hash[2] == 1: mammal = 1 # rule 3 4 if hash[3] == 1 or (hash[4] == 1 and hash[5] == 1): bird = 1 # rule 5 6 if hash[6] == 1 or (hash[7] == 1 and hash[8] == 1 and hash[9] == 1): meat = 1 # rule 7 8 if mammal == 1 and (hash[10] == 1 or hash[11] == 1): foot = 1 # rule 9 if mammal == 1 and meat == 1 and hash[12] == 1 and hash[13] == 1: if check == 0: check = 1 result = "豹" # rule 10 if mammal == 1 and meat == 1 and hash[12] == 1 and hash[14] == 1: if check == 0: check = 1 result = "虎" # rule 11 if foot == 1 and hash[15] == 1 and hash[16] == 1 and hash[13] == 1: if check == 0: check = 1 result = "长颈鹿" # rule 12 if foot == 1 and hash[14] == 1: if check == 0: check = 1 result = "斑马" # rule 13 if bird == 1 and hash[17] == 1 and hash[15] == 1 and hash[16] == 1 and hash[18] == 1: if check == 0: check = 1 result = "鸵鸟" # rule 14 if bird == 1 and hash[17] == 1 and hash[19] == 1 and hash[18] == 1: if check == 0: check = 1 result = "企鹅" # rule 15 if bird == 1 and hash[20] == 1: if check == 0: check = 1 result = "信天翁" if check == 1: print("判断的结果是:"+result) else: print("无法判断") |
2.2:实验过程与结果
在实验过程中,首先编写供用户查阅编号和对应特征的字典,然后令用户根据提示输入特征的总数和每个特征的编号,中间使用哈希表将用户输入的特征所对应的表内位置设定为1,不涉及的特征设定为0,再通过if语句逐条判断规则是否成立,如果成立则将相应的判定结果进行标记,最后输出判断的结果。
值得注意的是,有可能出现无法判断的情况。以下将展示测试规则系统中的各类判断结果,并逐个列举用户所使用的特征。
用户字典:

·测试豹:1、2、6、7、8、9、12、13

·测试虎:1、2、6、7、8、9、12、14

·测试斑马:1、2、10、11、14、17、19

·测试长颈鹿:1、10、13、15、16

·测试企鹅:3、5、17、18、19

·测试鸵鸟:3、5、15、16、17、18

·测试信天翁:3、20

·测试无法判断:1、3、6

综上所述,各类情况均判断完毕,结果如图所示。
五、遇到的问题和解决办法
问题1:
| n = int(input("please input the total number of your features: ")) # add int() to convert str into int, or error will occur for i in range(n): t = int(input("please input your current feature number: ")) feature.append(t) |
上述代码在没有加int()前,input默认输入的为字符串,导致在循环开头时,n不是整数类型而报错。
解决方法1:
将 n = input() 改为 n = int(input()) 即可。

![命令行输入sns.countplot(data[‘marital‘])报错](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/3cf264ddc4f940f7a44b3a57b3847ee8.png)





