注:实验工具为jupyter,该python环境为3.7并安装了1.14.0版本的tensorflow ,这是本人基于最新版的anaconda下新建的环境,至于在头歌环境平台及其他平台并未验证,而我们需要安装和更新包也需要在自己新建的环境命令行下才有效。
//这里建议大家先打开主菜单,找到anaconda,打开315电脑上名为tf的jupyter,在这里面进行代码运行,如果需要安装包,也请在名为tf下的prompt里面输入命令。
第一步:把源代码里的文件放到相关路径下
本人这里放到了C:\Users\D415,也就是jupyter运行结果的保存路径,因为我后面统一设置路径为.\。为节约时间,以下代码的generations统一设置为500

//也可以在jupyter页面直接导入,或者更改源代码里面的对应路径
7.2TensorFlow实现简单的CNN
//pip install 包名 -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple/ (提高安装效率)
pip install matplotlibimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
from tensorflow.python.framework import ops
ops.reset_default_graph()
# 创建计算图
sess = tf.Session()
# 加载数据集
data_dir = 'temp'
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets(data_dir, one_hot=False)
# 将图像数据转换成28*28的数组
train_xdata = np.array([np.reshape(x, (28, 28)) for x in mnist.train.images])
test_xdata = np.array([np.reshape(x, (28, 28)) for x in mnist.test.images])
# 将数据预处理成独热编码
train_labels = mnist.train.labels
test_labels = mnist.test.labels
# 设置模型参数
batch_size = 100
learning_rate = 0.001
evaluation_size = 500
image_width = train_xdata[0].shape[0]
image_height = train_xdata[0].shape[1]
target_size = np.max(train_labels) + 1
num_channels = 1 # greyscale = 1 channel
generations = 500#次数
eval_every = 5
conv1_features = 25
conv2_features = 50
max_pool_size1 = 2 # NxN window for 1st max pool layer
max_pool_size2 = 2 # NxN window for 2nd max pool layer
fully_connected_size1 = 100
# 声明模型占位符
x_input_shape = (batch_size, image_width, image_height, num_channels)
x_input = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=x_input_shape)
y_target = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, shape=(batch_size))
eval_input_shape = (evaluation_size, image_width, image_height, num_channels)
eval_input = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=eval_input_shape)
eval_target = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, shape=(evaluation_size))
# 声明模型卷积层权重值参数和偏置值
conv1_weight = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([4, 4, num_channels, conv1_features],
stddev=0.1, dtype=tf.float32))
conv1_bias = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([conv1_features], dtype=tf.float32))
conv2_weight = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([4, 4, conv1_features, conv2_features],
stddev=0.1, dtype=tf.float32))
conv2_bias = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([conv2_features], dtype=tf.float32))
# 声明模型全连接层权重参数和偏置值
resulting_width = image_width // (max_pool_size1 * max_pool_size2)
resulting_height = image_height // (max_pool_size1 * max_pool_size2)
full1_input_size = resulting_width * resulting_height * conv2_features
full1_weight = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([full1_input_size,
fully_connected_size1],
stddev=0.1, dtype=tf.float32))
full1_bias = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([fully_connected_size1], stddev=0.1, dtype=tf.float32))
full2_weight = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([fully_connected_size1,
target_size], stddev=0.1, dtype=tf.float32))
full2_bias = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([target_size], stddev=0.1,
dtype=tf.float32))
# 初始化模型
def my_conv_net(conv_input_data):
# 第1层Conv-ReLU-MaxPool层
conv1 = tf.nn.conv2d(conv_input_data, conv1_weight,
strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
relu1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.bias_add(conv1, conv1_bias))
max_pool1 = tf.nn.max_pool(relu1, ksize=[1, max_pool_size1,
max_pool_size1, 1],
strides=[1, max_pool_size1, max_pool_size1, 1],
padding='SAME')
# 第2层Conv-ReLU-MaxPool层
conv2 = tf.nn.conv2d(max_pool1, conv2_weight, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1],
padding='SAME')
relu2 = tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.bias_add(conv2, conv2_bias))
max_pool2 = tf.nn.max_pool(relu2, ksize=[1, max_pool_size2,
max_pool_size2, 1],
strides=[1, max_pool_size2, max_pool_size2, 1],
padding='SAME')
# 将输出数据转换成方便全连接层接收的1*N形式
final_conv_shape = max_pool2.get_shape().as_list()
final_shape = final_conv_shape[1] * final_conv_shape[2] * final_conv_shape[3]
flat_output = tf.reshape(max_pool2, [final_conv_shape[0],
final_shape])
# 第1个全连接层
fully_connected1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.add(tf.matmul(flat_output,
full1_weight), full1_bias))
# 第2个全连接层
final_model_output = tf.add(tf.matmul(fully_connected1,
full2_weight), full2_bias)
return final_model_output
model_output = my_conv_net(x_input)
test_model_output = my_conv_net(eval_input)
# 指定损失函数为softmax函数为损失函数
loss = tf.reduce_mean(
tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(
logits=model_output, labels=y_target))
# 指定准确度函数以评估模型精度
prediction = tf.nn.softmax(model_output)
test_prediction = tf.nn.softmax(test_model_output)
# 创建准确度函数。
def get_accuracy(logits, targets):
batch_predictions = np.argmax(logits, axis=1)
num_correct = np.sum(np.equal(batch_predictions, targets))
return 100. * num_correct/batch_predictions.shape[0]
# 创建优化器
my_optimizer = tf.train.MomentumOptimizer(learning_rate, 0.9)
train_step = my_optimizer.minimize(loss)
# 初始化变量
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess.run(init)
# 开始训练
train_loss = []
train_acc = []
test_acc = []
for i in range(generations):
rand_index = np.random.choice(len(train_xdata), size=batch_size)
rand_x = train_xdata[rand_index]
rand_x = np.expand_dims(rand_x, 3)
rand_y = train_labels[rand_index]
train_dict = {x_input: rand_x, y_target: rand_y}
sess.run(train_step, feed_dict=train_dict)
temp_train_loss, temp_train_preds = sess.run([loss, prediction], feed_dict=train_dict)
temp_train_acc = get_accuracy(temp_train_preds, rand_y)
if (i+1) % eval_every == 0:
eval_index = np.random.choice(len(test_xdata), size=evaluation_size)
eval_x = test_xdata[eval_index]
eval_x = np.expand_dims(eval_x, 3)
eval_y = test_labels[eval_index]
test_dict = {eval_input: eval_x, eval_target: eval_y}
test_preds = sess.run(test_prediction, feed_dict=test_dict)
temp_test_acc = get_accuracy(test_preds, eval_y)
# 记录并输出结果
train_loss.append(temp_train_loss)
train_acc.append(temp_train_acc)
test_acc.append(temp_test_acc)
acc_and_loss = [(i+1), temp_train_loss, temp_train_acc, temp_test_acc]
acc_and_loss = [np.round(x, 2) for x in acc_and_loss]
print('Generation # {}. Train Loss: {:.2f}. Train Acc (Test Acc): {:.2f} ({:.2f})'.format(*acc_and_loss))
# 通过Matlotlib模块绘制损失函数和准确度
eval_indices = range(0, generations, eval_every)
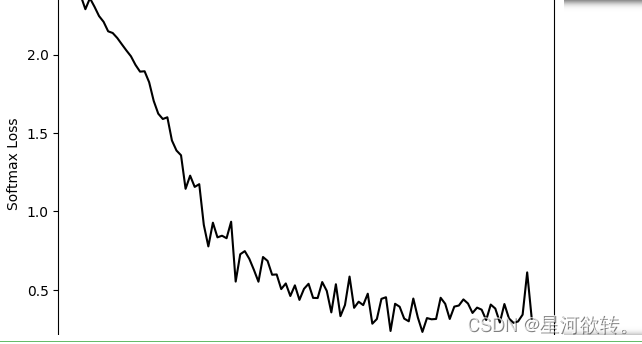
plt.plot(eval_indices, train_loss, 'k-')
plt.title('Softmax Loss per Generation')
plt.xlabel('Generation')
plt.ylabel('Softmax Loss')
plt.show()
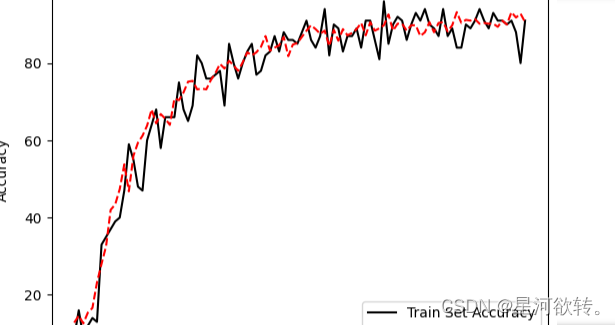
plt.plot(eval_indices, train_acc, 'k-', label='Train Set Accuracy')
plt.plot(eval_indices, test_acc, 'r--', label='Test Set Accuracy')
plt.title('Train and Test Accuracy')
plt.xlabel('Generation')
plt.ylabel('Accuracy')
plt.legend(loc='lower right')
plt.show()
# 输出最新结果中的抽样图(此处选取了4幅)
actuals = rand_y[0:4]
predictions = np.argmax(temp_train_preds, axis=1)[0:4]
images = np.squeeze(rand_x[0:4])
Nrows = 2
Ncols = 3
for i in range(4):
plt.subplot(Nrows, Ncols, i+1)
plt.imshow(np.reshape(images[i], [28, 28]), cmap='Greys_r')
plt.title('Actual: ' + str(actuals[i]) + ' Pred: ' +
str(predictions[i]),
fontsize=10)
frame = plt.gca()
frame.axes.get_xaxis().set_visible(False)
frame.axes.get_yaxis().set_visible(False)
运行结果展示: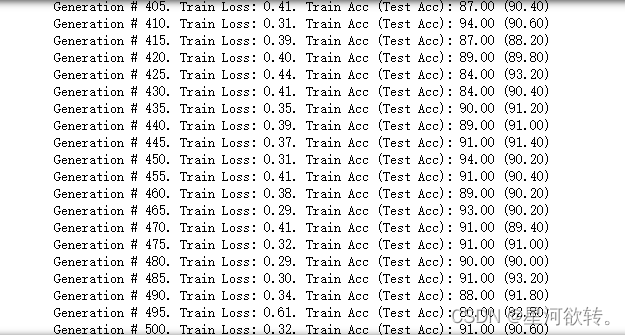

7.2TensorFlow实现进阶CNN
import os
import sys
import tarfile
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from six.moves import urllib
from tensorflow.python.framework import ops
ops.reset_default_graph()
sess = tf.Session()
batch_size = 128
data_dir = 'temp'
output_every = 50
generations = 500
eval_every = 500
image_height = 32
image_width = 32
crop_height = 24
crop_width = 24
num_channels = 3
num_targets = 10
extract_folder = 'cifar-10-batches-bin'
learning_rate = 0.1
lr_decay = 0.1
num_gens_to_wait = 250.0
image_vec_length = image_height * image_width * num_channels
record_length = 1 + image_vec_length # ( + 1 for the 0-9 label)
data_dir = 'temp'
def read_cifar_files(filename_queue, distort_images = True):
reader = tf.FixedLengthRecordReader(record_bytes=record_length)
key, record_string = reader.read(filename_queue)
record_bytes = tf.decode_raw(record_string, tf.uint8)
image_label = tf.cast(tf.slice(record_bytes, [0], [1]), tf.int32)
# 读取图片
image_extracted = tf.reshape(tf.slice(record_bytes, [1],
[image_vec_length]),
[num_channels, image_height, image_width])
# 调整图片的规格
image_uint8image = tf.transpose(image_extracted, [1, 2, 0])
reshaped_image = tf.cast(image_uint8image, tf.float32)
# 随机裁剪图片
final_image = tf.image.resize_image_with_crop_or_pad(reshaped_image,
crop_width, crop_height)
if distort_images:
# 对图片进行随机的剪裁、翻转和亮度调节
final_image = tf.image.random_flip_left_right(final_image)
final_image = tf.image.random_brightness(final_image,max_delta=63)
final_image = tf.image.random_contrast(final_image,lower=0.2, upper=1.8)
# 白化处理去除各观测信号之间的相关性
final_image = tf.image.per_image_standardization(final_image)
return(final_image, image_label)
def input_pipeline(batch_size, train_logical=True):
if train_logical:
files = [os.path.join(data_dir, extract_folder, 'data_batch_{}.bin'.format(i)) for i in range(1,6)]
else:
files = [os.path.join(data_dir, extract_folder, 'test_batch.bin')]
filename_queue = tf.train.string_input_producer(files)
image, label = read_cifar_files(filename_queue)
#通过min_after_dequeue参数设置抽样图片缓存最小值
min_after_dequeue = 5000
capacity = min_after_dequeue + 3 * batch_size
#tf.train.batch表示样本和样本标签, batch_size是返回的一个batch样本集的
#样本个数。capacity是队列中的容量。这主要是按顺序组合成一个batch。
example_batch, label_batch = tf.train.shuffle_batch([image, label],batch_size=batch_size, capacity=capacity,min_after_dequeue=min_after_dequeue)
return(example_batch, label_batch)
def cifar_cnn_model(input_images, batch_size, train_logical=True):
def truncated_normal_var(name, shape, dtype):
return(tf.get_variable(name=name, shape=shape, dtype=dtype, initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=0.05)))
def zero_var(name, shape, dtype):
return(tf.get_variable(name=name, shape=shape, dtype=dtype, initializer=tf.constant_initializer(0.0)))
# 第一层卷积层
with tf.variable_scope('conv1') as scope:
# 卷积核尺寸为5x5对应3个色彩通道,创建64个特征
conv1_kernel = truncated_normal_var(name='conv_kernel1', shape=[5, 5, 3, 64], dtype=tf.float32)
# 设定卷积操作的步长值为1
conv1 = tf.nn.conv2d(input_images, conv1_kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
# 初始化并添加偏置项
conv1_bias = zero_var(name='conv_bias1', shape=[64], dtype=tf.float32)
conv1_add_bias = tf.nn.bias_add(conv1, conv1_bias)
# 指定激活函数为ReLU函数
relu_conv1 = tf.nn.relu(conv1_add_bias)
# 最大池化操作
pool1 = tf.nn.max_pool(relu_conv1, ksize=[1, 3, 3, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1],padding='SAME', name='pool_layer1')
# 局部响应归一化
norm1 = tf.nn.lrn(pool1, depth_radius=5, bias=2.0, alpha=1e-3, beta=0.75, name='norm1')
# 第二层卷积层
with tf.variable_scope('conv2') as scope:
# 卷积核规格为5x5, 再次创建64个特征
conv2_kernel = truncated_normal_var(name='conv_kernel2', shape=[5, 5, 64, 64], dtype=tf.float32)
# 指定卷积操作的步长值为1
conv2 = tf.nn.conv2d(norm1, conv2_kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
# 初始化参数并添加偏置项
conv2_bias = zero_var(name='conv_bias2', shape=[64], dtype=tf.float32)
conv2_add_bias = tf.nn.bias_add(conv2, conv2_bias)
# 指定激活函数为ReLU函数
relu_conv2 = tf.nn.relu(conv2_add_bias)
# 最大池化
pool2 = tf.nn.max_pool(relu_conv2, ksize=[1, 3, 3, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME', name='pool_layer2')
# 局部响应归一化
norm2 = tf.nn.lrn(pool2, depth_radius=5, bias=2.0, alpha=1e-3, beta=0.75, name='norm2')
# 调整输出数据的格式以适应全连接层
reshaped_output = tf.reshape(norm2, [batch_size, -1])
reshaped_dim = reshaped_output.get_shape()[1].value
# 第一层全连接层
with tf.variable_scope('full1') as scope:
# 指定384个节点
full_weight1 = truncated_normal_var(name='full_mult1',
shape=[reshaped_dim, 384], dtype=tf.float32)
full_bias1 = zero_var(name='full_bias1', shape=[384],
dtype=tf.float32)
full_layer1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.add(tf.matmul(reshaped_output,
full_weight1), full_bias1))
# 第二个全连接层
with tf.variable_scope('full2') as scope:
# 指定192个节点.
full_weight2 = truncated_normal_var(name='full_mult2',
shape=[384, 192], dtype=tf.float32)
full_bias2 = zero_var(name='full_bias2', shape=[192],
dtype=tf.float32)
full_layer2 = tf.nn.relu(tf.add(tf.matmul(full_layer1,
full_weight2), full_bias2))
# 第三层全连接层,将第二层全连接层的192个节点连接到10个输出分类
with tf.variable_scope('full3') as scope:
full_weight3 = truncated_normal_var(name='full_mult3', shape=[192, num_targets], dtype=tf.float32)
full_bias3 = zero_var(name='full_bias3',
shape=[num_targets], dtype=tf.float32)
final_output = tf.add(tf.matmul(full_layer2,
full_weight3), full_bias3)
return(final_output)
def cifar_loss(logits, targets):
# Get rid of extra dimensions and cast targets into integers
targets = tf.squeeze(tf.cast(targets, tf.int32))
# 计算评估值与目标值的Sofltmax交叉熵
cross_entropy = tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=logits, labels=targets)
# 求解基于batch size的平均损失值
cross_entropy_mean = tf.reduce_mean(cross_entropy, name='cross_entropy')
return(cross_entropy_mean)
def train_step(loss_value, generation_num):
model_learning_rate = tf.train.exponential_decay(learning_rate,generation_num, num_gens_to_wait, lr_decay, staircase=True)
my_optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(model_learning_rate)
train_step = my_optimizer.minimize(loss_value)
return(train_step)
def accuracy_of_batch(logits, targets):
# 指定目标向量为整数型,并去除extra dimensions
targets = tf.squeeze(tf.cast(targets, tf.int32))
# 获取logit 回归最大的值作为预测值
batch_predictions = tf.cast(tf.argmax(logits, 1), tf.int32)
# 确保不同batch间的值相等
predicted_correctly = tf.equal(batch_predictions, targets)
# 计算准确度
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(predicted_correctly, tf.float32))
return(accuracy)
# 初始化图像管道
images, targets = input_pipeline(batch_size, train_logical=True)
# 从图像管道获取测试图像和目标图像的batch
test_images, test_targets = input_pipeline(batch_size, train_logical=False)
with tf.variable_scope('model_definition') as scope:
# 声明训练网络模型
model_output = cifar_cnn_model(images, batch_size)
# 通过scope.reuse_variables()保存模型的参数,方便以后重用
scope.reuse_variables()
test_output = cifar_cnn_model(test_images, batch_size)
#声明损失函数
loss = cifar_loss(model_output, targets)
#声明准确度函数
accuracy = accuracy_of_batch(test_output, test_targets)
#声明命迭代变量
generation_num = tf.Variable(0, trainable=False)
train_op = train_step(loss, generation_num)
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess.run(init)
tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess=sess)
train_loss = []
test_accuracy = []
for i in range(generations):
_, loss_value = sess.run([train_op, loss])
if (i+1) % output_every == 0:
train_loss.append(loss_value)
output = 'Generation {}: Loss = {:.5f}'.format((i+1), loss_value)
print(output)
if (i+1) % eval_every == 0:
[temp_accuracy] = sess.run([accuracy])
test_accuracy.append(temp_accuracy)
acc_output = ' --- Test Accuracy = {:.2f}%.'.format(100.*temp_accuracy)
print(acc_output)
eval_indices = range(0, generations, eval_every)
output_indices = range(0, generations, output_every)
plt.plot(output_indices, train_loss, 'k-')
plt.title('Softmax Loss per Generation')
plt.xlabel('Generation')
plt.ylabel('Softmax Loss')
plt.show()
plt.plot(eval_indices, test_accuracy, 'k-')
plt.title('Test Accuracy')
plt.xlabel('Generation')
plt.ylabel('Accuracy')
plt.show()
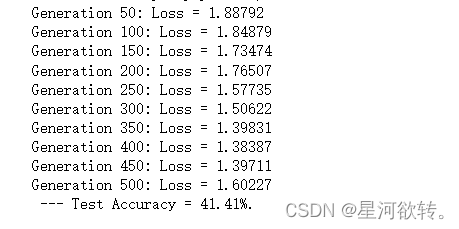
运行结果展示:


7.4实现图片风格渲染
pip install scipy
pip install imgaug这里源代码并不能展示图片,下面给出由吴金龙同学改进的代码:
import os
import scipy.io
import scipy.misc
import imageio.v2 as imageio
from skimage.transform import resize
from operator import mul
from functools import reduce
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.python.framework import ops
ops.reset_default_graph()
# 指定原始图片与风格图片的文件夹
original_image_file = r'.\images\cover.jpg'
style_image_file = r'.\images\starry_night.jpg'
# 设置模型参数
vgg_path = r'.\imagenet-vgg-verydeep-19.mat'
original_image_weight = 5.0
style_image_weight = 500.0
regularization_weight = 100
learning_rate = 10
generations = 500
output_generations = 25
beta1 = 0.9
beta2 = 0.999
# 读取图片
original_image = imageio.imread(original_image_file)
style_image = imageio.imread(style_image_file)
# 获取目标规格并使风格图像与之相同
target_shape = original_image.shape
style_image = resize(style_image, target_shape)
# 设置VGG-19 Layer
vgg_layers = ['conv1_1', 'relu1_1',
'conv1_2', 'relu1_2', 'pool1',
'conv2_1', 'relu2_1',
'conv2_2', 'relu2_2', 'pool2',
'conv3_1', 'relu3_1',
'conv3_2', 'relu3_2',
'conv3_3', 'relu3_3',
'conv3_4', 'relu3_4', 'pool3',
'conv4_1', 'relu4_1',
'conv4_2', 'relu4_2',
'conv4_3', 'relu4_3',
'conv4_4', 'relu4_4', 'pool4',
'conv5_1', 'relu5_1',
'conv5_2', 'relu5_2',
'conv5_3', 'relu5_3',
'conv5_4', 'relu5_4']
# 提取权重和矩阵方法
def extract_net_info(path_to_params):
vgg_data = scipy.io.loadmat(path_to_params)
normalization_matrix = vgg_data['normalization'][0][0][0]
mat_mean = np.mean(normalization_matrix, axis=(0,1))
network_weights = vgg_data['layers'][0]
return mat_mean, network_weights
# 创建VGG-19 神经网络
def vgg_network(network_weights, init_image):
network = {}
image = init_image
for i, layer in enumerate(vgg_layers):
if layer[0] == 'c':
weights, bias = network_weights[i][0][0][0][0]
weights = np.transpose(weights, (1, 0, 2, 3))
bias = bias.reshape(-1)
conv_layer = tf.nn.conv2d(image, tf.constant(weights), (1, 1, 1, 1), 'SAME')
image = tf.nn.bias_add(conv_layer, bias)
elif layer[0] == 'r':
image = tf.nn.relu(image)
else: # pooling
image = tf.nn.max_pool(image, (1, 2, 2, 1), (1, 2, 2, 1), 'SAME')
network[layer] = image
return network
# 定义将哪一层网络用于原始图片还是风格图片
original_layers = ['relu4_2', 'relu5_2']
style_layers = ['relu1_1', 'relu2_1', 'relu3_1', 'relu4_1', 'relu5_1']
# 获取网络的参数
normalization_mean, network_weights = extract_net_info(vgg_path)
shape = (1,) + original_image.shape
style_shape = (1,) + style_image.shape
original_features = {}
style_features = {}
# 设置风格权重
style_weights = {l: 1./(len(style_layers)) for l in style_layers}
# 计算原始图片的特征值
g_original = tf.Graph()
with g_original.as_default(), tf.Session() as sess1:
image = tf.placeholder('float', shape=shape)
vgg_net = vgg_network(network_weights, image)
original_minus_mean = original_image - normalization_mean
original_norm = np.array([original_minus_mean])
for layer in original_layers:
original_features[layer] = vgg_net[layer].eval(feed_dict={image: original_norm})
# 获取风格图片的网络层
g_style = tf.Graph()
with g_style.as_default(), tf.Session() as sess2:
image = tf.placeholder('float', shape=style_shape)
vgg_net = vgg_network(network_weights, image)
style_minus_mean = style_image - normalization_mean
style_norm = np.array([style_minus_mean])
for layer in style_layers:
features = vgg_net[layer].eval(feed_dict={image: style_norm})
features = np.reshape(features, (-1, features.shape[3]))
gram = np.matmul(features.T, features) / features.size
style_features[layer] = gram
# 根据损失值进行图片的合并
with tf.Graph().as_default():
# 获取网络参数
initial = tf.random_normal(shape) * 0.256
init_image = tf.Variable(initial)
vgg_net = vgg_network(network_weights, init_image)
# 原始图片的损失值
original_layers_w = {'relu4_2': 0.5, 'relu5_2': 0.5}
original_loss = 0
for o_layer in original_layers:
temp_original_loss = original_layers_w[o_layer] * original_image_weight *\
(2 * tf.nn.l2_loss(vgg_net[o_layer] - original_features[o_layer]))
original_loss += (temp_original_loss / original_features[o_layer].size)
# 风格图片的损失值
style_loss = 0
style_losses = []
for style_layer in style_layers:
layer = vgg_net[style_layer]
feats, height, width, channels = [x.value for x in layer.get_shape()]
size = height * width * channels
features = tf.reshape(layer, (-1, channels))
style_gram_matrix = tf.matmul(tf.transpose(features), features) / size
style_expected = style_features[style_layer]
style_losses.append(style_weights[style_layer] * 2 *
tf.nn.l2_loss(style_gram_matrix - style_expected) /
style_expected.size)
style_loss += style_image_weight * tf.reduce_sum(style_losses)
total_var_x = reduce(mul, init_image[:, 1:, :, :].get_shape().as_list(), 1)
total_var_y = reduce(mul, init_image[:, :, 1:, :].get_shape().as_list(), 1)
first_term = regularization_weight * 2
second_term_numerator = tf.nn.l2_loss(init_image[:, 1:, :, :] - init_image[:, :shape[1]-1, :, :])
second_term = second_term_numerator / total_var_y
third_term = (tf.nn.l2_loss(init_image[:, :, 1:, :] - init_image[:, :, :shape[2]-1, :]) / total_var_x)
total_variation_loss = first_term * (second_term + third_term)
# 合并后的损失值
loss = original_loss + style_loss + total_variation_loss
# 声明算法操作
optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate, beta1, beta2)
train_step = optimizer.minimize(loss)
# 初始化全部变量并开始操作
with tf.Session() as sess:
tf.global_variables_initializer().run()
for i in range(generations):
train_step.run()
# 输出跟新并保存最新的输出
if (i+1) % output_generations == 0:
print('Generation {} out of {}, loss: {}'.format(i + 1, generations,sess.run(loss)))
image_eval = init_image.eval()
best_image_add_mean = image_eval.reshape(shape[1:]) + normalization_mean
output_file = r'.\temp_output_{}.jpg'.format(i)
if best_image_add_mean.shape != (1, 1, 437, 690, 3):
# 如果形状不正确,则需要进行调整
best_image_add_mean = np.reshape(best_image_add_mean, (437, 690, 3))
# 检查调整后的形状
if best_image_add_mean.shape == (437, 690, 3):
# 如果调整后的形状正确,则继续处理
pass
else:
# 如果调整后的形状仍然不正确,则引发异常
raise ValueError("Array shape is not valid.")
else:
# 如果形状正确,则不需要进行调整
best_image_add_mean = np.squeeze(best_image_add_mean)
# 将数组转换为float32类型
best_image_add_mean = best_image_add_mean.astype(np.float32)
# 转换数组类型
best_image_add_mean = (best_image_add_mean * 255).astype(np.uint8)
# 调整数组形状
best_image_add_mean = np.transpose(best_image_add_mean, (2, 0, 1))
# 创建PIL图像对象
pil_image = Image.fromarray(best_image_add_mean.transpose(1, 2, 0))
# 保存图像
pil_image.save(output_file)
# 保存最终图片
image_eval = init_image.eval()
best_image_add_mean = image_eval.reshape(shape[1:]) + normalization_mean
output_file = r'.\final_output.jpg'
best_image_add_mean = best_image_add_mean.astype(np.float32)
if best_image_add_mean.shape != (1, 1, 437, 690, 3):
# 如果形状不正确,则需要进行调整
best_image_add_mean = np.reshape(best_image_add_mean, (437, 690, 3))
# 检查调整后的形状
if best_image_add_mean.shape == (437, 690, 3):
# 如果调整后的形状正确,则继续处理
pass
else:
# 如果调整后的形状仍然不正确,则引发异常
raise ValueError("Array shape is not valid.")
else:
# 如果形状正确,则不需要进行调整
best_image_add_mean = np.squeeze(best_image_add_mean)
# 将数组转换为float32类型
best_image_add_mean = best_image_add_mean.astype(np.float32)
# 转换数组类型
best_image_add_mean = (best_image_add_mean * 255).astype(np.uint8)
# 调整数组形状
best_image_add_mean = np.transpose(best_image_add_mean, (2, 0, 1))
# 创建PIL图像对象
pil_image = Image.fromarray(best_image_add_mean.transpose(1, 2, 0))
# 保存图像
pil_image.save(output_file)修改方法:
1.对应地址位置要修改
2.将import imageio改为import imageio.v2 as imageio
3.加入from PIL import Image
4.将两处的imageio.imwrite(output_file, best_image_add_mean)
修改为
if best_image_add_mean.shape != (1, 1, 437, 690, 3):
# 如果形状不正确,则需要进行调整
best_image_add_mean = np.reshape(best_image_add_mean, (437, 690, 3))
# 检查调整后的形状
if best_image_add_mean.shape == (437, 690, 3):
# 如果调整后的形状正确,则继续处理
pass
else:
# 如果调整后的形状仍然不正确,则引发异常
raise ValueError("Array shape is not valid.")
else:
# 如果形状正确,则不需要进行调整
best_image_add_mean = np.squeeze(best_image_add_mean)
# 将数组转换为float32类型
best_image_add_mean = best_image_add_mean.astype(np.float32)
# 转换数组类型
best_image_add_mean = (best_image_add_mean * 255).astype(np.uint8)
# 调整数组形状
best_image_add_mean = np.transpose(best_image_add_mean, (2, 0, 1))
# 创建PIL图像对象
pil_image = Image.fromarray(best_image_add_mean.transpose(1, 2, 0))
# 保存图像
pil_image.save(output_file)
运行在对应位置可以找到对应位置
//漏斗标志表示程序正在运行
运行结果展示:(由于运行次数较小,所以图片较为模糊)