C语言CRC-16 CCITT格式校验函数
CRC-16校验产生2个字节长度的数据校验码,通过计算得到的校验码和获得的校验码比较,用于验证获得的数据的正确性。基本的CRC-16校验算法实现,参考: C语言标准CRC-16校验函数。
不同同应用规范通过对输入数据前处理和输出数据后处理的方式不同,又产生了不同的应用规范校验函数,这里介绍CCITT格式的CRC-16校验函数。CCITT格式对输入数据,按照单个字节进行位反序。对于输出的校验码,进行整体位反序。
生成多项式为x^16 + x^12 + x^5 + 1
正向算法
正向算法是符合标准CRC-16的计算理论,从左向右计算,也即计算过程中移位时,向左移出。几种正向算法的实现如下:
CRC-16 CCITT格式校验函数一(8位输入数据格式,64位装载计算):
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
uint16_t PY_CRC_16_CCITT(uint8_t *di, uint32_t len)
{
uint32_t crc_poly = 0x00011021; //X^16+X^12+X^5+1 total 17 effective bits. Computed total data shall be compensated 16-bit '0' before CRC computing.
uint8_t *datain;
uint64_t cdata = 0; //Computed total data
uint32_t data_t = 0; //Process data of CRC computing
uint16_t index_t = 63; ///bit shifting index for initial '1' searching
uint16_t index = 63; //bit shifting index for CRC computing
uint8_t rec = 0; //bit number needed to be compensated for next CRC computing
uint32_t cn=(len+2)/6;
uint32_t cr=(len+2)%6;
uint32_t j;
datain = malloc(len+2);
for(j=0;j<len;j++)
{
datain[j] = 0;
for(uint8_t m=0; m<=7; m++)
{
datain[j] |= ( ( di[j]>>(7-m) ) & 1 ) << m;
}
}
datain[len] = 0; datain[len+1] = 0;//Compensate 16-bit '0' for input data
if(len<=6) //Mount data for only one segment
{
for(j=0;j<=(len+1);j++)
{
cdata = (cdata<<8);
cdata = cdata|datain[j];
}
cn = 1;
}
else
{
if(cr==0)
{
cr = 6;
}
else if(cr==1)
{
cr = 7;
}
else if(cr==2)
{
cr = 8;
}
else
{
cn++;
}
for(j=0;j<cr;j++)
{
cdata = (cdata<<8);
cdata = cdata|datain[j];
}
}
do
{
cn--;
while(index_t>0)
{
if( (cdata>>index_t)&1 )
{
index = index_t;
index_t = 0;
data_t |= (cdata>>(index-16));
{
data_t = data_t ^ crc_poly;
}
while((index!=0x5555)&&(index!=0xaaaa))
{
for(uint8_t n=1;n<17;n++)
{
if ((data_t>>(16-n))&1) {rec = n;break;}
if (n==16) rec=17;
}
if((index-16)<rec)
{
data_t = data_t<<(index-16);
data_t |= (uint32_t)((cdata<<(64-(index-16)))>>(64-(index-16)));
index = 0x5555;
}
else
{
for(uint8_t i=1;i<=rec;i++)
{
data_t = (data_t<<1)|((cdata>>(index-16-i))&1) ;
}
if(rec!= 17)
{
data_t = data_t ^ crc_poly;
index -= rec;
}
else
{
data_t = 0;
index_t = index-16-1;
index = 0xaaaa;
}
}
}
if(index==0x5555) break;
}
else
{
index_t--;
if(index_t<16) break;
}
}
if(cn>0) //next segment
{
cdata = data_t&0x00ffff;
for(uint8_t k=0;k<6;k++)
{
cdata = (cdata<<8);
cdata = cdata|datain[j++];
}
data_t = 0;
index_t = 63; ///bit shifting index for initial '1' searching
index = 63; //bit shifting index for CRC computing
rec = 0; //bit number needed to be compensated for next CRC computing
}
}
while(cn>0);
free(datain);
uint16_t i_data_t = 0;
for(uint8_t n=0; n<=15; n++)
{
i_data_t |= ( ( data_t>>(15-n) ) & 1 ) << n;
}
return i_data_t;
}
CRC-16 CCITT格式校验函数二(8位输入数据格式):
uint16_t PY_CRC_16_S_CCITT(uint8_t *di, uint32_t len)
{
uint16_t crc_poly = 0x1021; //X^16+X^12+X^5+1 total 16 effective bits without X^16. Computed total data shall be compensated 16-bit '0' before CRC computing.
uint32_t clen = len+2;
uint8_t cdata[clen] ;
for(uint32_t j=0;j<len;j++)
{
cdata[j] = 0;
for(uint8_t m=0; m<=7; m++)
{
cdata[j] |= ( ( di[j]>>(7-m) ) & 1 ) << m;
}
}
cdata[len]=0; cdata[len+1]=0;
uint16_t data_t = (((uint16_t)cdata[0]) << 8) + cdata[1]; //CRC register
for (uint32_t i = 2; i < clen; i++)
{
for (uint8_t j = 0; j <= 7; j++)
{
if(data_t&0x8000)
data_t = ( (data_t<<1) | ( (cdata[i]>>(7-j))&0x01) ) ^ crc_poly;
else
data_t = ( (data_t<<1) | ( (cdata[i]>>(7-j))&0x01) ) ;
}
}
uint16_t i_data_t = 0;
for(uint8_t n=0; n<=15; n++)
{
i_data_t |= ( ( data_t>>(15-n) ) & 1 ) << n;
}
return i_data_t;
}
CRC-16 CCITT格式校验函数三(16位输入数据格式):
uint16_t PY_CRC_16_T16_CCITT(uint16_t *di, uint32_t len)
{
uint16_t crc_poly = 0x1021; //X^16+X^12+X^5+1 total 16 effective bits without X^16.
uint16_t data_t = 0; //CRC register
uint16_t cdata[len];
for(uint32_t j=0;j<len;j++)
{
cdata[j] = 0;
for(uint8_t m=0; m<=7; m++)
{
cdata[j] |= ( ( ( (di[j]>>8)>>(7-m) ) & 1 ) << m ) | ( ( ( ( (di[j]&0x00ff)>>(7-m) ) & 1 ) << m ) <<8 );
}
}
for(uint32_t i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
data_t ^= cdata[i]; //16-bit data
for (uint8_t j = 0; j < 16; j++)
{
if (data_t & 0x8000)
data_t = (data_t << 1) ^ crc_poly;
else
data_t <<= 1;
}
}
uint16_t i_data_t = 0;
for(uint8_t n=0; n<=15; n++)
{
i_data_t |= ( ( data_t>>(15-n) ) & 1 ) << n;
}
return i_data_t;
}
CRC-16 CCITT格式校验函数四(8位输入数据格式):
uint16_t PY_CRC_16_T8_CCITT(uint8_t *di, uint32_t len)
{
uint16_t crc_poly = 0x1021; //X^16+X^12+X^5+1 total 16 effective bits without X^16.
uint16_t data_t = 0; //CRC register
uint8_t cdata[len];
for(uint32_t j=0;j<len;j++)
{
cdata[j] = 0;
for(uint8_t m=0; m<=7; m++)
{
cdata[j] |= ( ( di[j]>>(7-m) ) & 1 ) << m;
}
}
for(uint32_t i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
data_t ^= cdata[i]<<8; //8-bit data
for (uint8_t j = 0; j < 8; j++)
{
if (data_t & 0x8000)
data_t = (data_t << 1) ^ crc_poly;
else
data_t <<= 1;
}
}
uint16_t i_data_t = 0;
for(uint8_t n=0; n<=15; n++)
{
i_data_t |= ( ( data_t>>(15-n) ) & 1 ) << n;
}
return i_data_t;
}
反向算法
反向算法是从由右向左计算,也即计算过程中移位时,向右移出。而计算过程中的输入数据高优先计算位和校验参数的对齐关系不变。因此把一个字节放在CRC计算寄存器的最低字节时,对于CCITT格式,最右侧最低位实际上是高优先计算位,而校验参数要相应倒序,从而计算位置对照关系不变。
CRC-16 CCITT格式校验函数五(反向算法,8位输入数据格式):
uint16_t PY_CRC_16_T8_CCITT_i(uint8_t *di, uint32_t len)
{
uint16_t crc_poly = 0x8408; //Bit sequence inversion of 0x1021
uint16_t data_t = 0; //CRC register
for(uint32_t i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
data_t ^= di[i]; //8-bit data
for (uint8_t j = 0; j < 8; j++)
{
if (data_t & 0x0001)
data_t = (data_t >> 1) ^ crc_poly;
else
data_t >>= 1;
}
}
return data_t;
}
算法验证
5种算法结果相同:
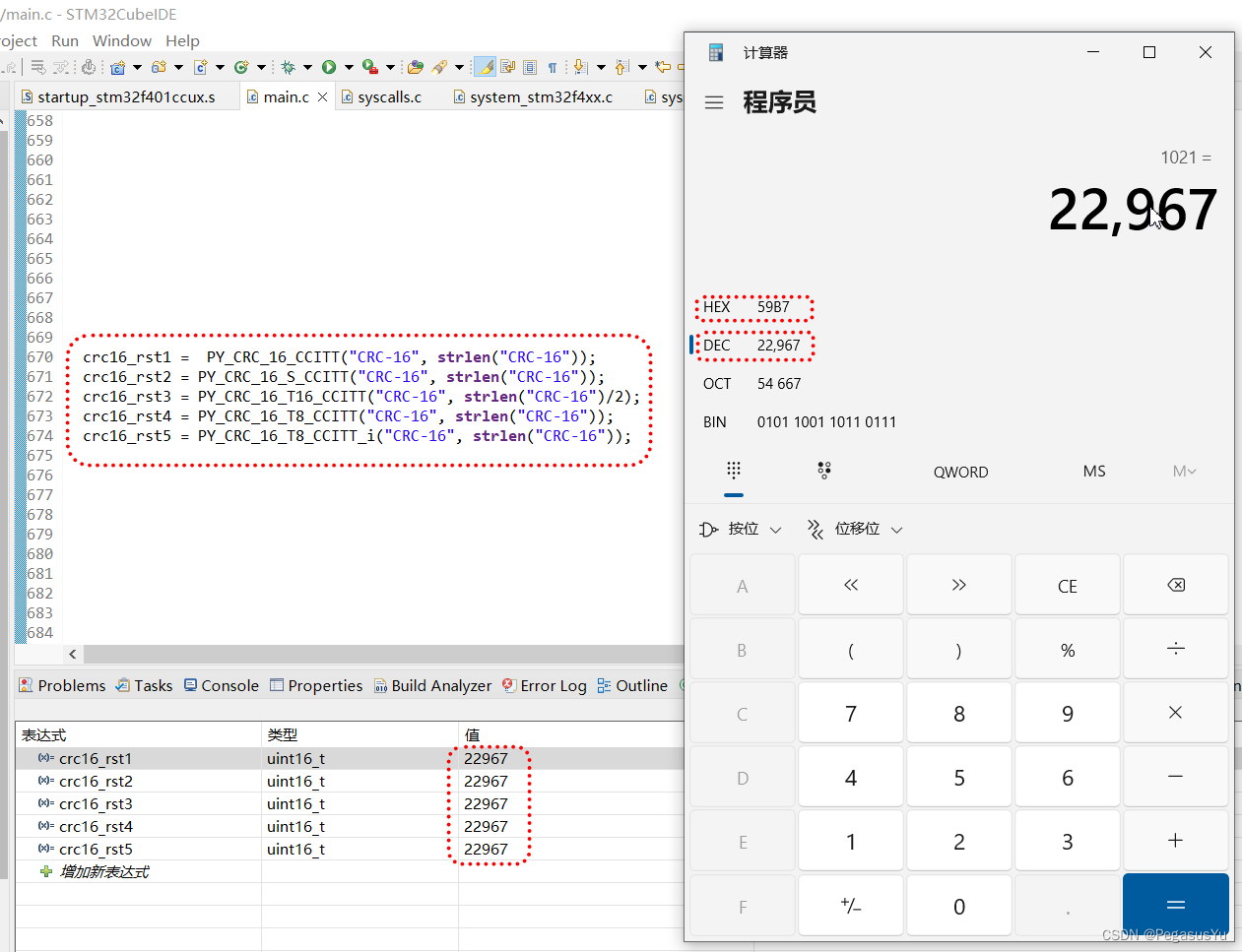
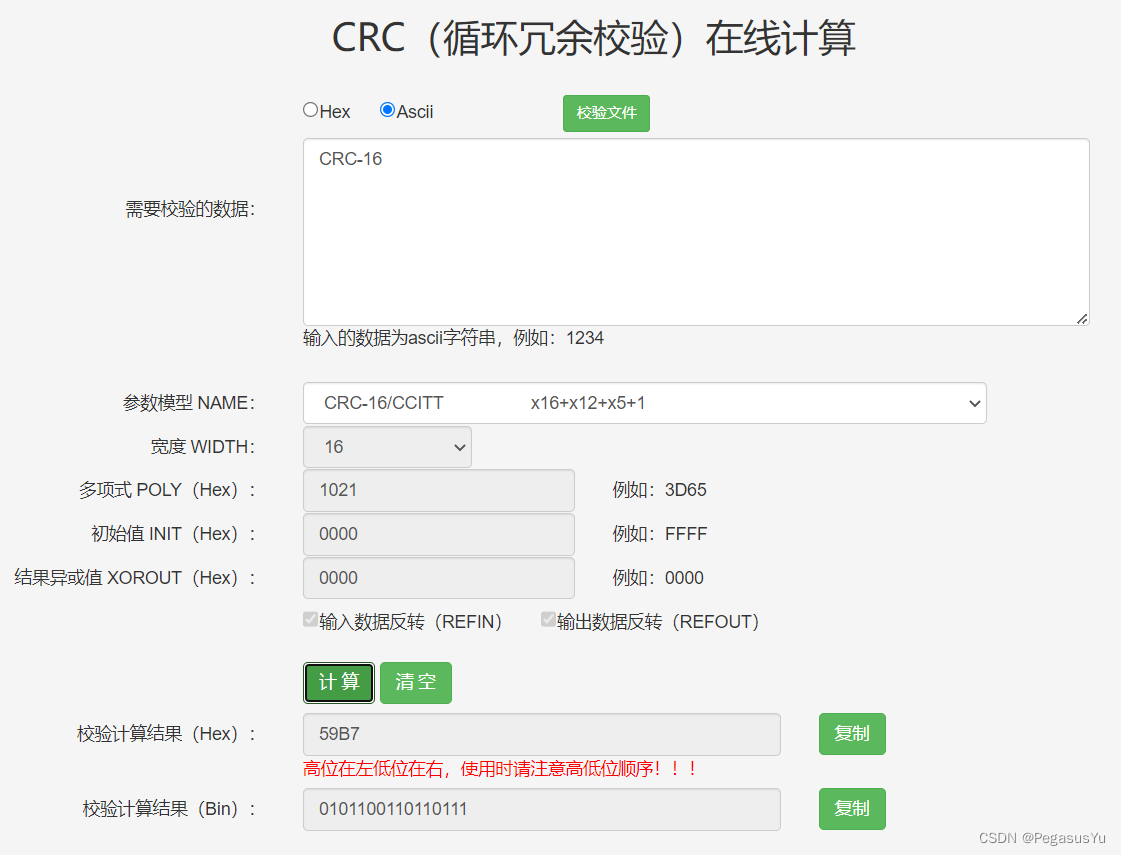
通过在线CRC工具对照验证成功:
–End–